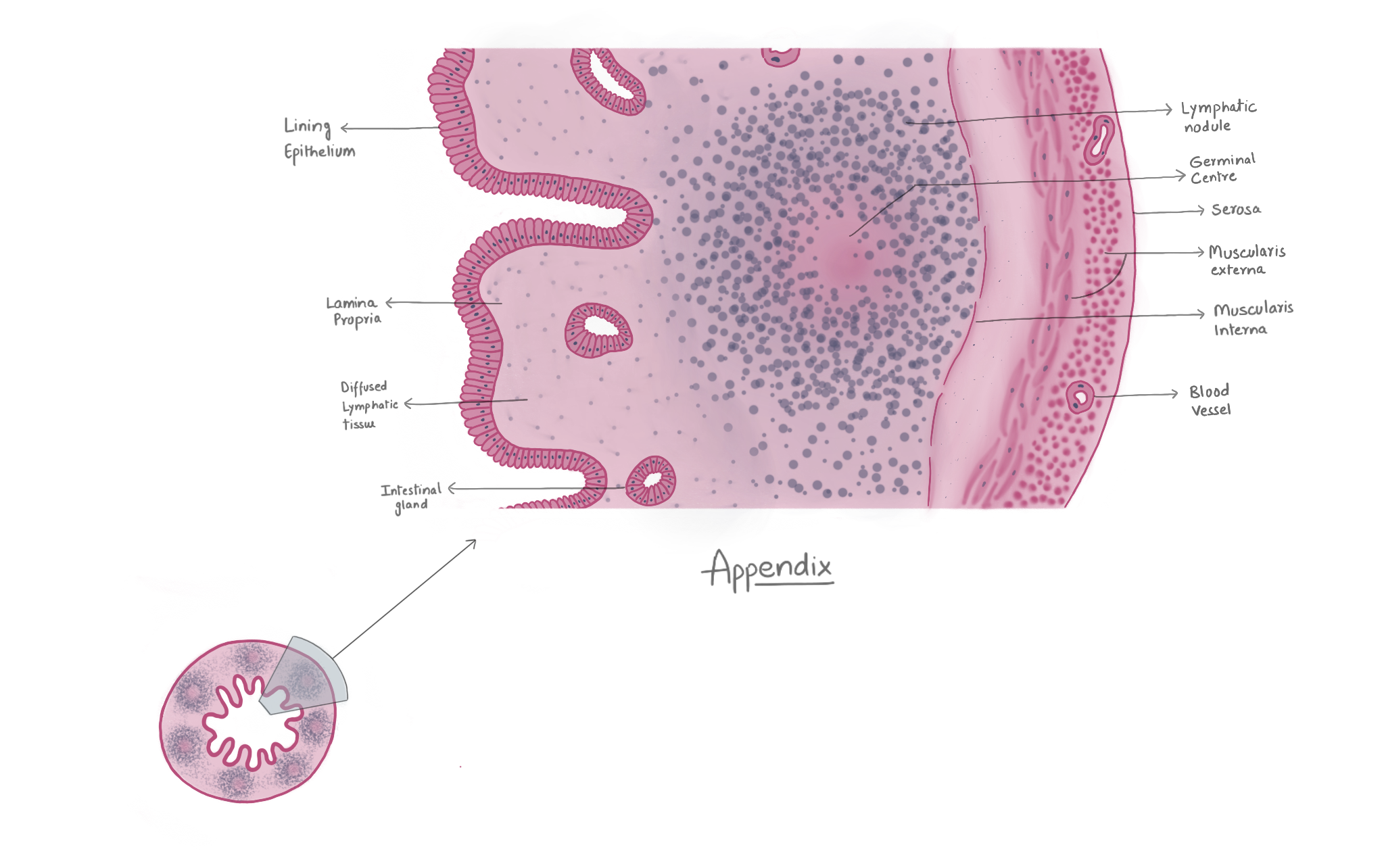
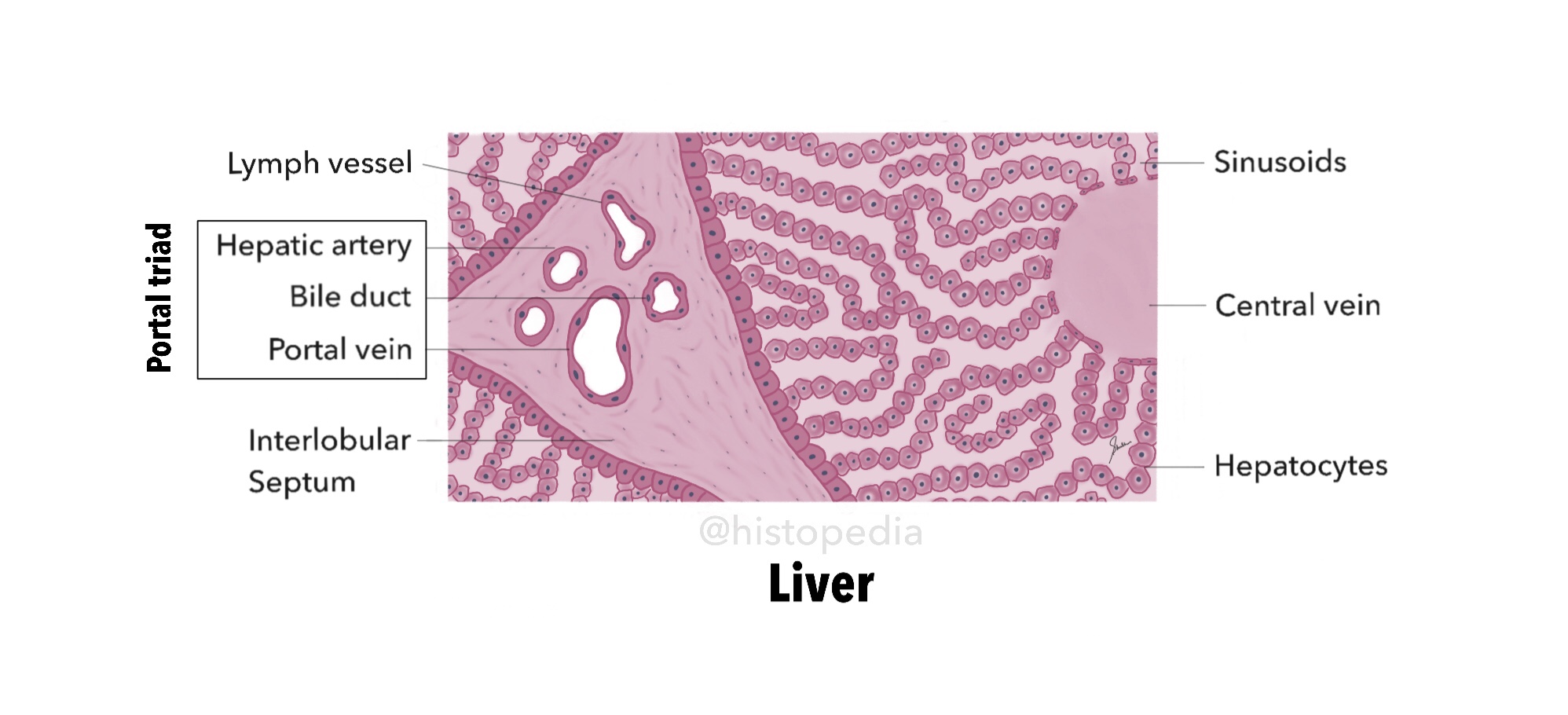
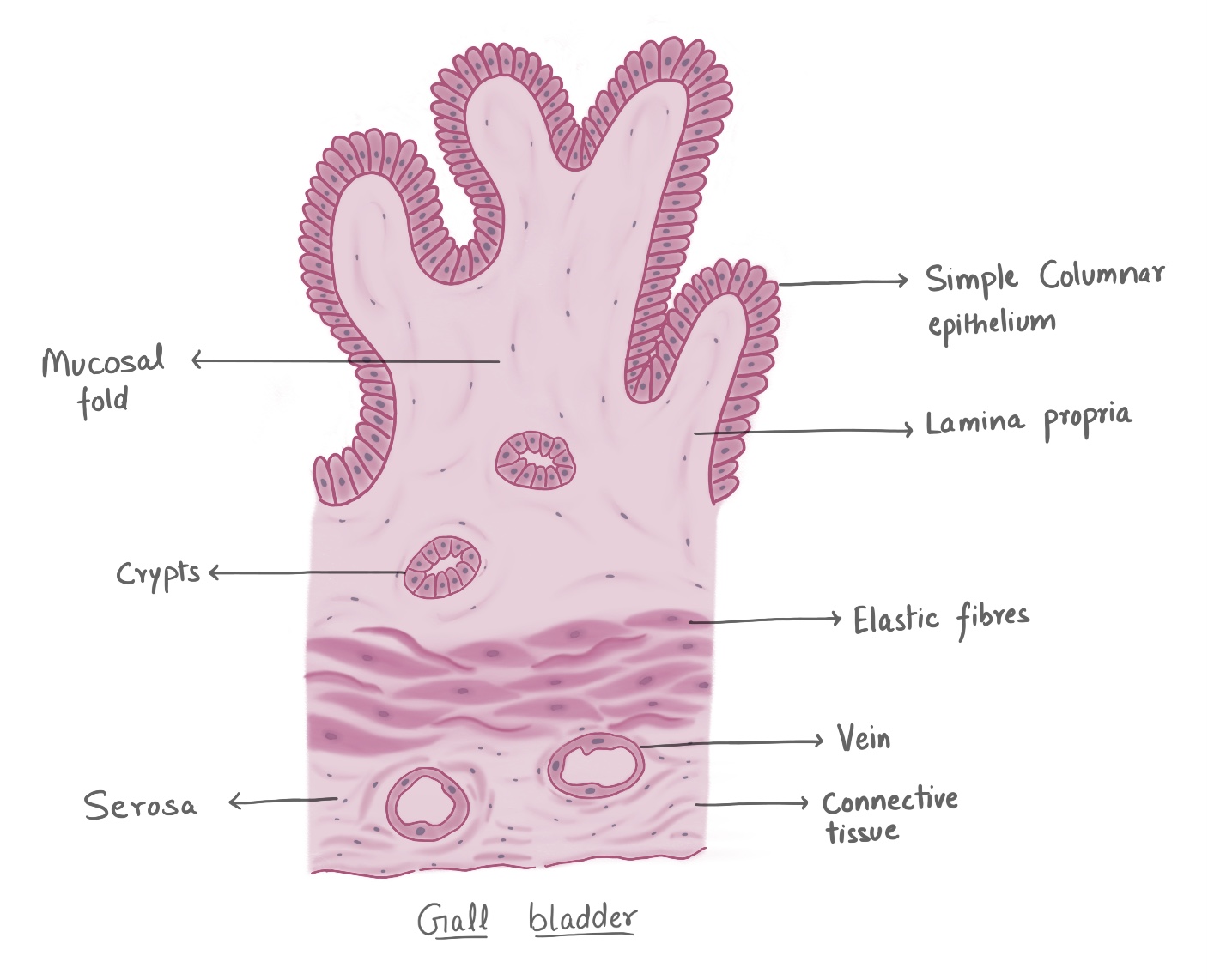
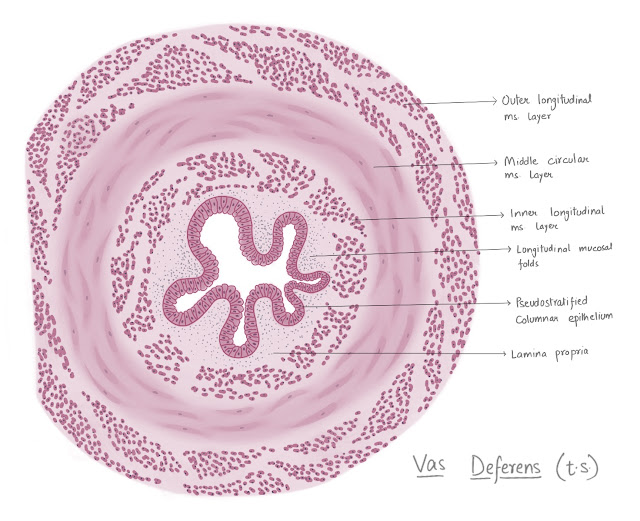
Parotid Salivary Gland

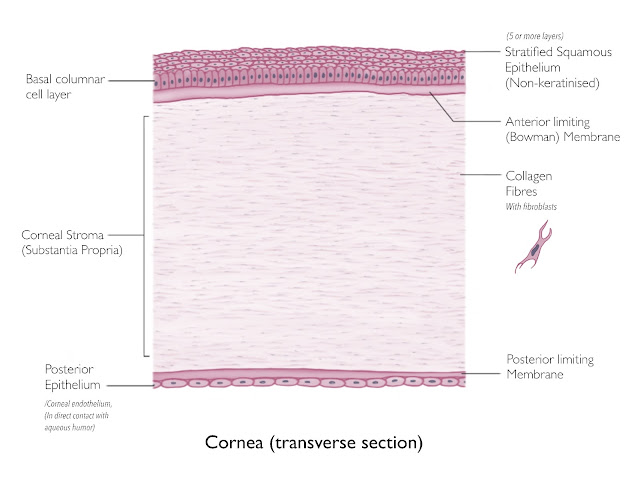
Identification Points: 1. Serous acini (pyramid shaped secretory cells with round basal nucleus) 2. No Serous Demilune 3. Striated Ducts Description: It is a large capsulated serous gland, subdivided into lobes and lobules by connective tissue septa located just anterior to the ears. It secretes 25% of total saliva which is serous (watery) in nature. At higher magnifications small secretory granules are visible in apices of serous acini Flow of Secretions: Serous acini (secretions) ⤵️ Intercalated ducts ⤵️ Striated Ducts (lined with Simple Columnar Cells ) ⤵️ Intra-lobular ducts ⤵️ Interlobular duct ( Pseudo-Stratified Columnar epithelium ) ⤵️ Stensen’s Duct (open near 2nd upper molar) Step-by-step Illustration: File Diagram: How to differentiate between all 3 Salivary Glands?