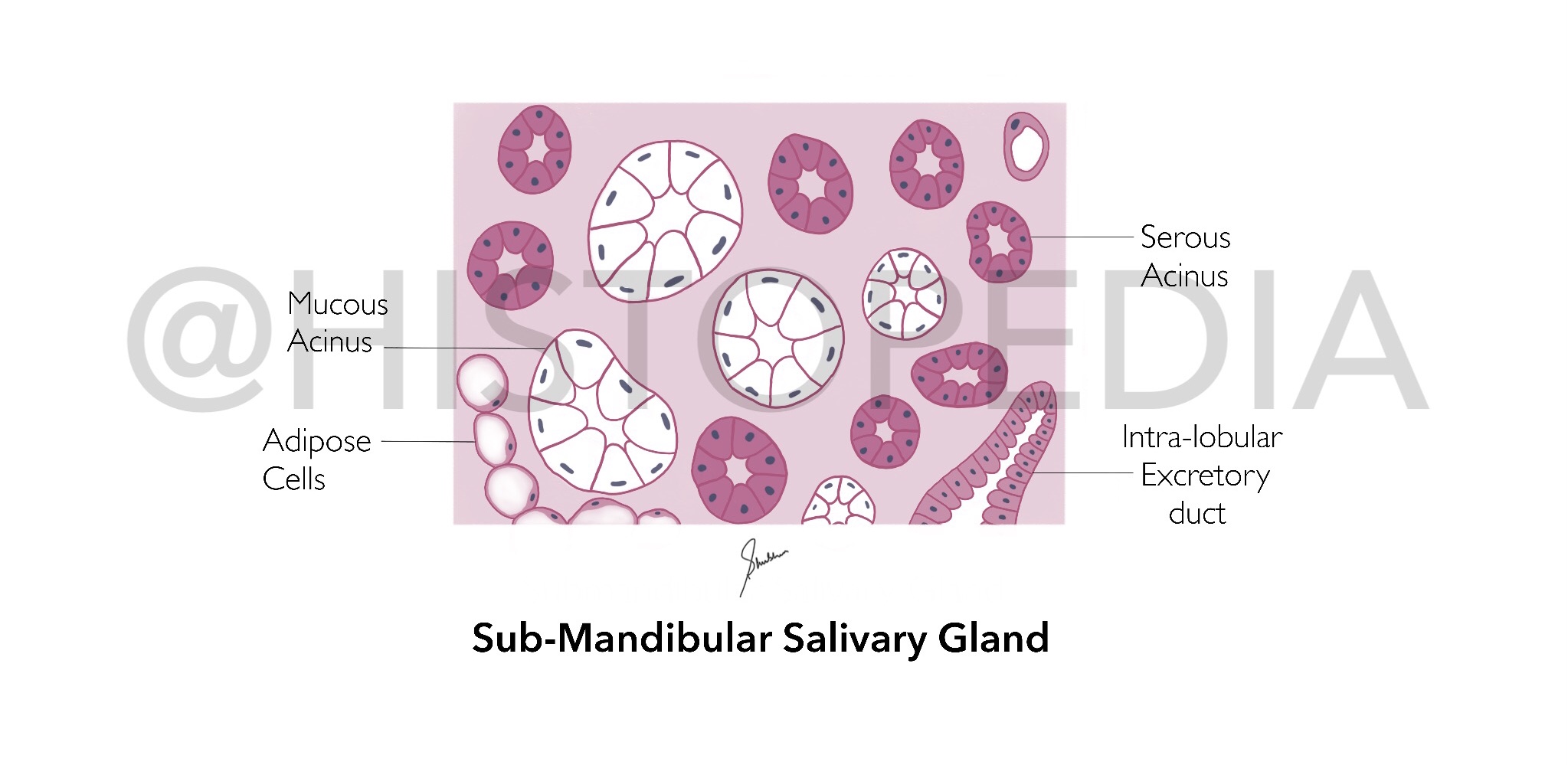
Sub-lingual Salivary Gland
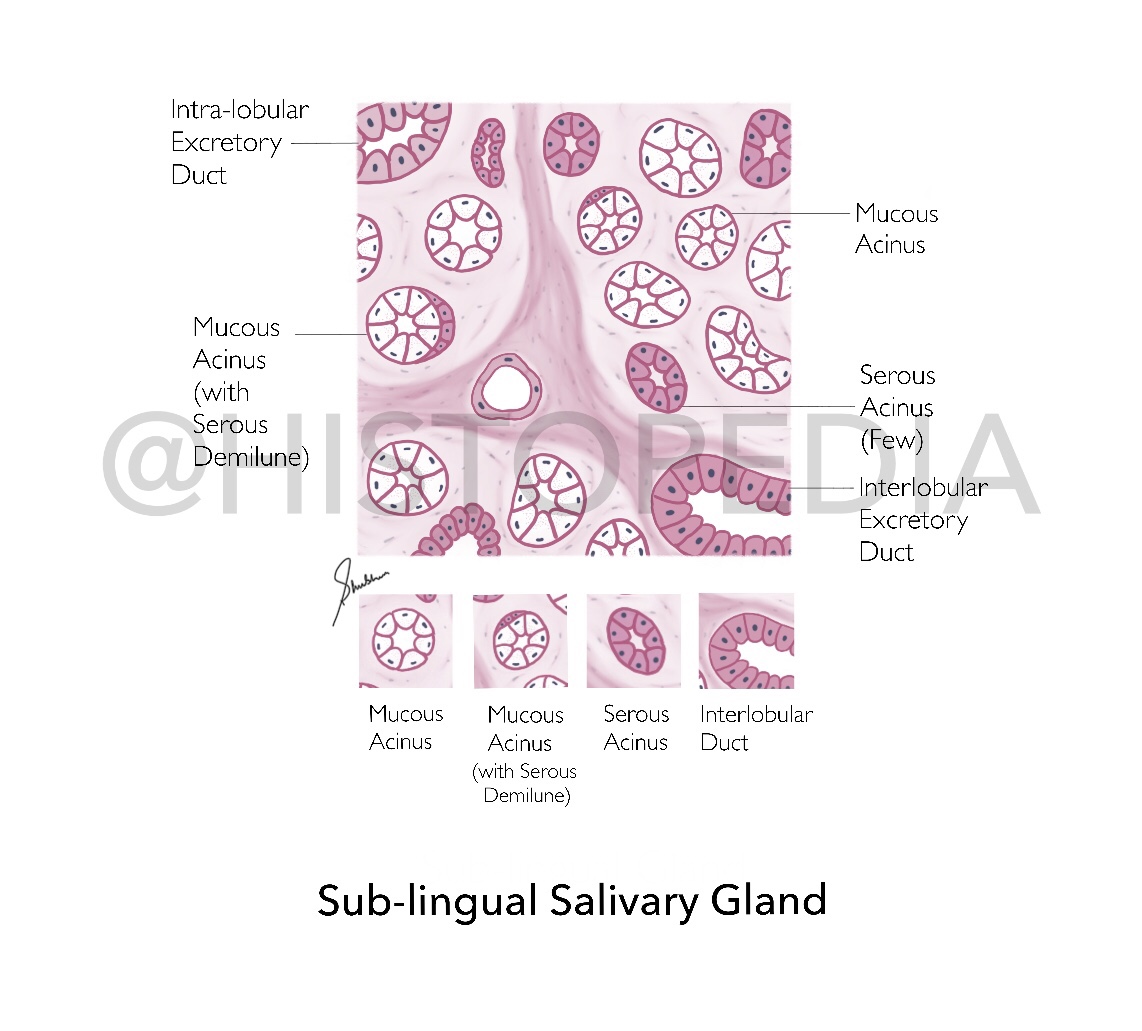
Identification Points: 1. Majority of acini are M ucous 2. Abundant Serous Demilunes [absent in Parotid Gland] 3. Intercalated ducts are short/absent (not readily observed) 4. Non-striated Intra-lobular ducts [differentiating factor from other 2 salivary glands] 5. Abundant Interlobular Connective tissue septa Description: It is a mixed type of salivary gland with both serous and mucous acini, most of which are mucous and capped with serous demilunes , It is responsible for 2-5% of saliva secretion which is mucoid in nature. It is smallest salivary gland, almond shaped located in the floor of oral cavity on either side of tongue. Flow of Secretions: Mucoid Secretions ⤵️ Non-striated Intra-lobular ducts (equivalent to striated ducts of other 2 salivary glands) ⤵️ Interlobular duct ⤵️ 8-20 excretory ducts (ducts of Rivinu) Step-by-step Illustration: File Diagram: How to differentiate betw...